The completely redesigned plan-apochromatic 20x/1.0 VIS-IR objective lens from Carl Zeiss now makes it possible to acquire 3D images of nerve cells down to depths of 5.6 mm in intact tissue using a confocal laser scanning or multiphoton microscope, without having to section the brain.
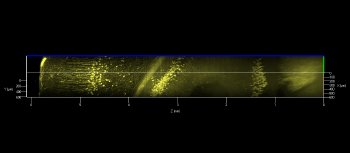
This permits the three-dimensional visualization of the branches of individual nerve cells and the imaging of their connections. In untreated tissue, the penetration depth now achievable is five to ten times more that of a multiphoton microscope featuring traditional optics.
Using the microscope to visualize and track nerve cells deep into the brain is an important step in the decoding of the brain circuitry. The new objective lens from Carl Zeiss now brings this goal considerably closer to realization. Carl Zeiss has designed the plan-apochromatic 20x/1.0 VIS-IR objective lens for the clearing method known as Scale developed by Dr. Atsushi Miyawaki at the RIKEN Brain Science Institute in Japan. A special water-based reagent solution transforms the sheath substance of the nerve cells into a transparent matrix without impairing the signals from fluorescent marker and tracer substances.
“I am very impressed by the new possibilities,” says Dr. Atsushi Miyawaki, whose results have been published in Nature Neuroscience and provoked broad interest in the neurosciences. In one of the most important research projects in the field of brain research, the Connectome project, the objective lens will help scientists obtain a better understanding of brain connectivity.
A prototype of the objective lens was presented at Neuroscience 2011 in Washington D.C. After concluding system tests, it will then become available for ZEISS confocal and multiphoton microscopes in 2012.